Covalent Architecture
Covalent consists of three component systems:
- A Python module containing an SDK that you use to build manageable workflows out of new or existing Python functions.
- A set of services that run locally or on a server to dispatch and execute workflow tasks.
- A browser-based UI from which to manage workflows and view results.
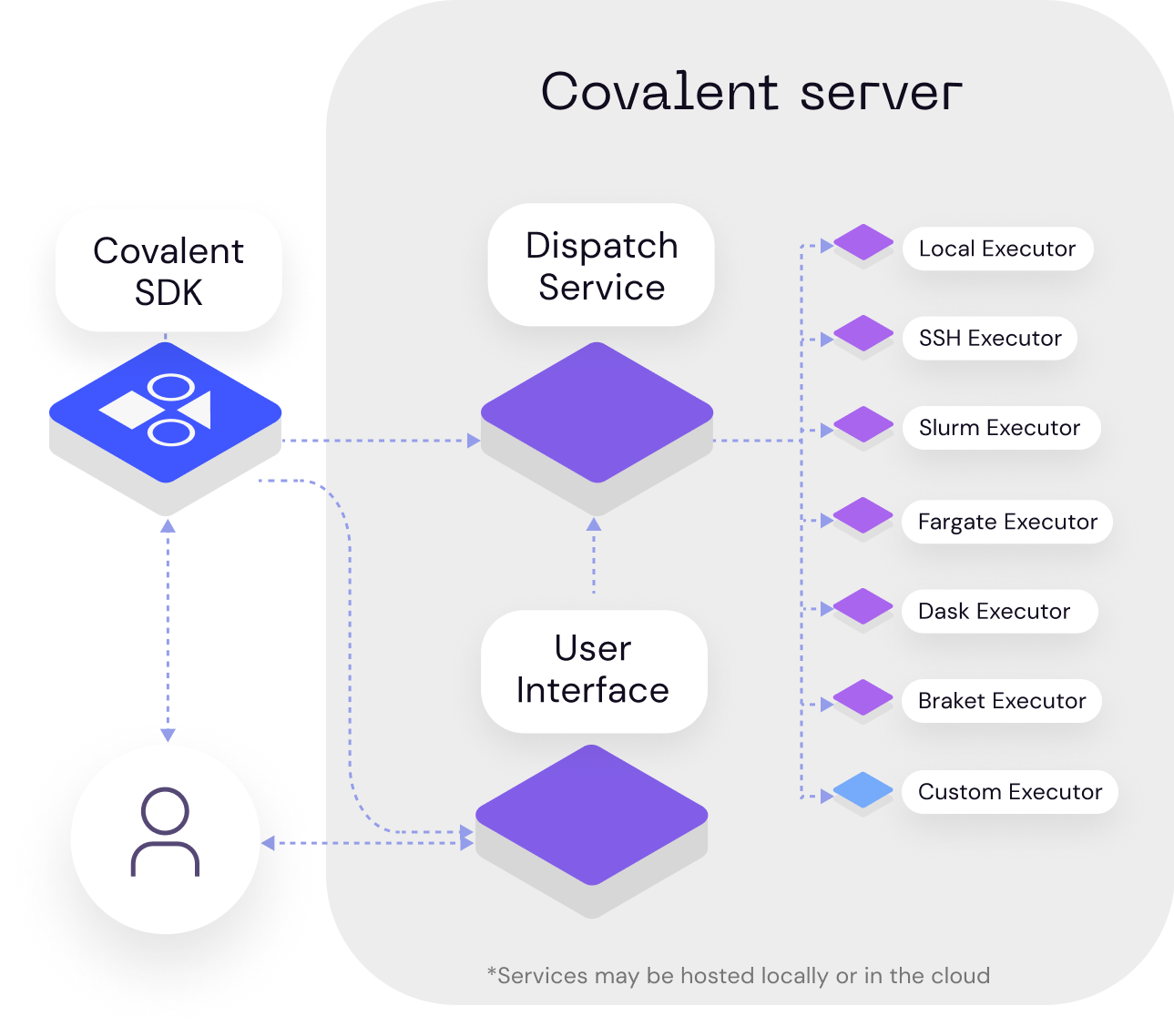
These components are briefly described below. A more detailed look at each component is presented in the linked pages.
The Covalent SDK
The Covalent API is a Python module containing a small collection of classes that implement server-based workflow management. The Covalent SDK is the subset of the API used to create and run workflows from Python code. The key elements are two decorators that wrap functions to create managed tasks and workflows.
The task decorator is called an electron. The electron decorator simply turns the function into a dispatchable task.
The workflow decorator is called a lattice. The lattice decorator turns a function composed of electrons into a manageable workflow.
For an in-depth description of the SDK, see The Covalent SDK.
Covalent Services
The Covalent server is a lightweight service that runs on your local machine or on a server. A dispatcher analyzes workflows (lattices) and hands its component tasks (electrons) off to executors. Each executor is an adaptor to a backend hardware resource. Covalent has a growing list of turn-key executors for common compute backends. If no executor exists yet for your compute platform, Covalent provides base classes for writing your own.
For an in-depth description of Covalent services, see Covalent Services.
The Covalent GUI
The Covalent graphical user interface (GUI) is a browser-based dashboard displayed by the dispatch service. Covalent keeps a database of dispatched workflows, and the GUI dashboard lists these dispatched workflows. From this list, you can select a single dispatched workflow and examine a graph and runtime details. You can also view logs, settings, and result sets.
For more about the Covalent GUI, see The Covalent GUI.